Metal frame structure building
The metal frame structure building is a combination of separate members that these members should be connected with each other in the right way. In fact, joints in metal buildings consist of various joints (such as the beam to the column and the column to the foundation and other joints to each other). Metal frame structures joints are called connecting elements (sheets, reinforcing parts, connecting sheets in nodes, angles, and connector gussets). The dimensions of the metal frame structure building should be designed in such a way that the calculated existing stress based on the structural analysis for the effective loads and the percentage of the strength of the members attached from the admissible stress become reduced.
Types of metal frame structure building joints
- Riveted joint
- Welding joint
- Screw joint
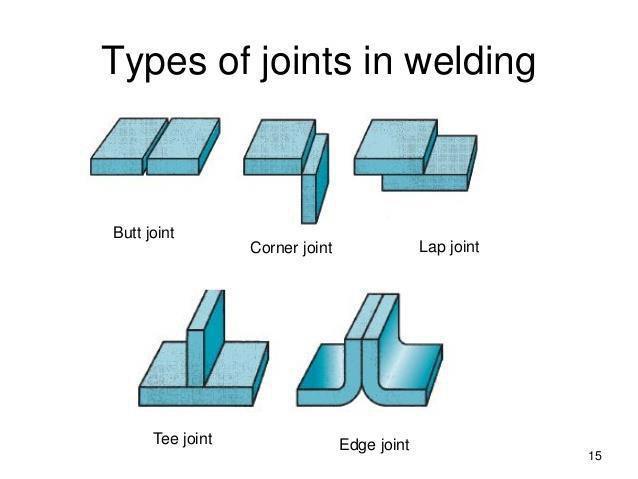
Types of weld joints
- Butt joint
- Lap joint
- T joint
- Corner joint
- Edge joint
Types of joints used in the projects
- Connect the column to the floor of the column
This type of connection is designed to transfer the existing forces at the foot of the column. For the axial compressive force, when the compression force is transmitted to the floor of the column through direct contact, the contact surface must be smooth and ready for compression transmission. In addition, there must be enough connection between the two pieces (the column and floor of the column) to be able to transfer forces during construction or any other possible force.
- Anchor transfer joint (anchor joint)
The connection of the ends of the beams, shafts and trusses, which require some rigidity in their supports, is an anchor joint.
- Beam to the column joint
These connections are of two types:
- Joint with Web Angle Pair:
Usually, they release connection pins of about 10 to 12 mm from the end of the beam, so that if the beam is about tolerance tolerated long, it can be installed without cutting its head and only by moving the angles.
- Joint with Seat Angle:
This connection is used for the reaction of beams of less than 15 tons. In these connections, a minimum fixity is made and the angles between the beam and the column are as free as possible. The seat angle makes it easy to install and adjustment of the beam. This angle is usually welded to the column at the required height, and then the beam rises and welds to it. In this connection, another auxiliary angle is installed and welded above the beam, which is only a fixing of the beam in its place and providing a cross support and preventing it from sliding. It tries to make the seat angle connection flexible as much as possible. In order to prevent the rotational freedom of the beam in the support, and in fact, it should be simple and articulated joint so that it does not create anchor at the support. Usually the width of the seat angle should not be less than 7.5 centimeters.
- Connect the console with the bracket:
At a time when the length of the console exceeds a specified limit or the amount of load is such that the connection of the angles with the gusset plate is not resistant, 45 degree brackets can be used. According to the architecture map, this bracket can be considered at the bottom or top, and made the connection in the right and principle way.
- Connect the two beams by angles:
First, to connect the two beams that are connected in the desired way to each other, you must use the tenon creation method. Welding and angle mode is usually used to connect the beam to the beam. Whatever the junction can be made fix, the vibration in the beam will be less and the problem will be solved. If the partially restrained connection is done, the consumption of profile will be economy.
Splice of compact members:
In the splice of the columns, the end section of the two pieces should be adjusted as smoothly as possible and, regardless of direct contact, splice and attachments should be adjusted so that the fastening parts are well kept in their place and desired axis. The splice must be able to withstand a force equal to the admissible capacity of the smaller connected member. The location of the splice column should be as far as possible from the connection of the beam to the column and stands in a region with little internal forces. All compact splices must be controlled to the tensile strength of the side loads (according to the building code 75% of dead load) without the effect of live load, so that the tensile stress is not exceeded beyond the amount of permission.
- Implementation of the pile under the shear wall:
In order to the shear wall to fully perform its task and to rigid the building in a position with respect to the lateral loads, it drill a borehole below the footing of shear wall and construct a pile to make a better joint.
Excavation and Foundation
At this stage, soil operations are carried out depending on the type of soil. It may be surface foundation; in this case, the excavation is carried out manually by the worker. In this method, at first the location of excavation is determined by plastering, and then the workers begin to dig the land, which is usually at depths of 1 meter. The excavated soil is usually sailed near the site, but in some cases it is necessary to be excavated and sanded in order to reach the suitable soil. In this case, hand-picking is not only possible, but also not cost-effective, and special equipment machinery must be used. In this case, the entire infrastructure of the building is excavated.
Safety issues during excavating:
- It is strictly forbidden to stand on top of the earth that is being rolled out. Because there is chance of falling apart of that part.
- The brace behind the wall should be firmly and standardized.
- In the case of a neighbor’s pad foundation, special arrangements must be made for the excavation by the supervisor engineer or the designer to prevent a differential settlement.
- It is advisable to detach parts next to the neighboring wall with a hand so that the impact of a power shovel or excavator loader does not hit the neighboring wall.
- Road-loaded soils are transported to outside of the city.
Piling:
Sometimes there is a suitable subgrade in the lower layers. In these cases, excavation and digging does not look so economical, so a more appropriate solution should be suggested. This more convenient solution can be to create wells and pilings. For piles, firstly, the wells are calculated in diameter (90 cm), then the grid is placed in a twisted bar net, and it is applied to concrete.
Foundation Reinforcement:
After digging and excavation, another layer of concrete, 150 kg / m2, is placed on the surface of the soil and then begin to reinforcement on it.
All bars, including longitudinal and transverse bars, stirrups, bar chair and etc, are cut and bent according to the operational plans and are ready to be put into work. Then the armature personnel start to reinforcement and laying them in the foundation.
To create a cover below the concrete segment of the grid, after preparing the bottom and the top mesh, apply a plate and base plate. In this case, the blades are welded to the bottom and top mesh after aligning and acquiring the center line panel. After welding the blades, place the plate on the blades. Be careful that the plate should be taken to put the plates on the requested alignment. This can be done with the camera.
Foundation formwork:
In this project, for the convenience and speed of the work, a metal form was used that was easily done and after concrete placement and acquiring concrete strength, the formwork was easily assembled.
Steel frame is a construction method with a “skeletal” frame of vertical and horizontal I-beam steel columns, built in a rectangular grid to support the floor, ceiling and walls of the building, all of which are connected to the frame. The development of this technique led to the construction of a skyscraper.
Implementation of the Joist block ceiling
Joists:
The most common type of joists in Iran is concrete joist, which are also used in this project. The joists are being constructed by the master craftsmen at the location of building. The joist construction formwork is made of downpipe profiles, which due to the ease of work, welds some of them together to increase the production process.
After completion of the work and the adhesion of concrete joist, the concrete is removed from the formwork and placed in the water pond, which is constructed on the construction site, so that the concrete gets more resistance in the vicinity of the water.
Block:
Blocks for the implementation of the joist and block ceiling are various modes such as clay, concrete, etc.
Implementation of the Joist and block ceiling
At first, the desired joists are selected and placed in the corresponding openings. It should be noted that the concrete section of the joist is destroyed at the beginning and the end so that the existing bar in the concrete is beamed so that during the laying of the concrete with the ceiling have a better connection between the joists. At the beginning, put the first beams of the span and then the next arc and put blocks between them, then the next joists and block. When this is done, only the first and end block of the span are placed so that only the joists can be adjusted. Depending on the opening, the roof less than 1 meter is kept with a profile or wooden beam to prevent the sagging of joists at intervals of 5. Then put metal and wooden pile under the beams and tighten them in place to withstand the weight of the consumed materials. It is better to put the used beams in place so that the middle of the joist is about 2 to 3 centimeters taller than the spirit level. This is also determined by structural engineer.
Temperature reinforcement
After finishing the roof and put all the desired ceiling joists and blocks, a series of bars have been put in the perpendicular direction to the joists at distances between 25 and 40 cm and the diameter is determined by calculation.